If acceleration as a function of time is known, then velocity and position functions can be derived using integral calculus. For constant acceleration, the integral equations refer to the first and second kinematic equations for velocity and position functions, respectively.
Consider an example to calculate the velocity and position from the acceleration function. A motorboat is traveling at a constant velocity of 5.0 m/s when it starts to decelerate to arrive at the dock. Its acceleration is −1/4·tm/s2. Let's determine the procedure to calculate the velocity and position function of the motorboat.
Let's take time, t = 0, when the boat starts to decelerate. Now, the velocity function can be calculated using the integral of the acceleration function

Using the expression of acceleration in the above equation, the velocity as a function of time is calculated to be

The constant of integration C1 is calculated to be 5 m/s using the value of initial time and velocity.
Hence, the velocity as a function of time reduces to

Integrating the derived velocity function with respect to time, the position function is calculated. The position as a function of time is
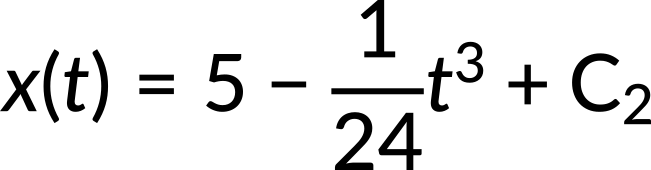
Again, using the initial conditions, the constant of integration C2 is calculated to be zero.
Thus, the position as a function of time reduces to

This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 3.6: Finding Velocity and Displacement from Acceleration.
From Chapter 3:

Now Playing
3.14 : Velocity and Position by Integral Method
Motion Along a Straight Line
5.8K Views

3.1 : الموقف والإزاحة
Motion Along a Straight Line
17.0K Views

3.2 : متوسط السرعة
Motion Along a Straight Line
17.9K Views

3.3 : السرعة اللحظية - أنا
Motion Along a Straight Line
12.2K Views

3.4 : السرعة اللحظية - II
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.0K Views

3.5 : متوسط التسارع
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.3K Views

3.6 : التسارع اللحظي
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.5K Views

3.7 : المعادلات الحركية - I
Motion Along a Straight Line
10.1K Views

3.8 : المعادلات الحركية - II
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.1K Views

3.9 : المعادلات الحركية - III
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.3K Views

3.10 : المعادلات الحركية: حل المشكلات
Motion Along a Straight Line
11.7K Views

3.11 : الأجسام المتساقطة بحرية: مقدمة
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.7K Views

3.12 : الأجسام المتساقطة بحرية: مثال
Motion Along a Straight Line
15.3K Views

3.13 : السرعة والموضع بالطريقة الرسومية
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.1K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved