3.8 : Equações Cinemáticas - II
The second kinematic equation expresses the final position of an object in terms of its initial position, the distance traveled with the initial constant velocity, and the distance traveled due to a change in velocity. Similar to the first kinematic equation, this equation is also only valid when the acceleration is constant throughout the motion of an object.
Suppose a car merges into freeway traffic on a 200 m long ramp. If its initial velocity is 10 m/s and it accelerates at 2 m/s2, then the time taken by the car to travel the 200 m long ramp can be calculated using the second kinematic equation. Here, the known quantities are the distance of 200 m, the initial velocity of the car of 10 m/s, and the acceleration of 2 m/s2. Using the second kinematic equation
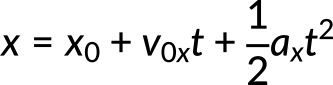
and substituting the known quantities in the above equation, we get

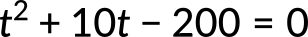
Using the quadratic formula to solve for time yields two solutions: t = 10 s and t = −20 s. A negative value for time is unreasonable, since that would mean the event happened 20 s before the motion began, therefore we can discard that solution. Thus, the time taken by the car to travel the 200 m ramp is 10 s.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 3.4: Motion with Constant Acceleration.
Do Capítulo 3:

Now Playing
3.8 : Equações Cinemáticas - II
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
9.3K Visualizações

3.1 : Posição e Deslocamento
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
17.2K Visualizações

3.2 : Velocidade Média
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
18.0K Visualizações

3.3 : Velocidade Instantânea - I
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
12.2K Visualizações

3.4 : Velocidade Instantânea - II
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
9.1K Visualizações

3.5 : Aceleração Média
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
9.4K Visualizações

3.6 : Aceleração Instantânea
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
7.5K Visualizações

3.7 : Equações Cinemáticas - I
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
10.2K Visualizações

3.9 : Equações Cinemáticas - III
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
7.4K Visualizações

3.10 : Equações Cinemáticas: Resolução de Problemas
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
11.8K Visualizações

3.11 : Corpos em Queda Livre: Introdução
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
8.0K Visualizações

3.12 : Corpos em Queda Livre: Exemplo
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
15.7K Visualizações

3.13 : Velocidade e Posição pelo Método Gráfico
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
7.2K Visualizações

3.14 : Velocidade e Posição pelo Método Integral
Movimento ao longo de uma linha reta
5.9K Visualizações
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos os direitos reservados