3.8 : Kinematic Equations - II
The second kinematic equation expresses the final position of an object in terms of its initial position, the distance traveled with the initial constant velocity, and the distance traveled due to a change in velocity. Similar to the first kinematic equation, this equation is also only valid when the acceleration is constant throughout the motion of an object.
Suppose a car merges into freeway traffic on a 200 m long ramp. If its initial velocity is 10 m/s and it accelerates at 2 m/s2, then the time taken by the car to travel the 200 m long ramp can be calculated using the second kinematic equation. Here, the known quantities are thedistance of 200 m, the initial velocity of the car of 10 m/s, and the acceleration of 2 m/s2. Using the second kinematic equation
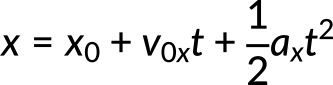
and substituting the known quantities in the above equation, we get

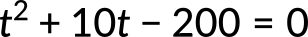
Using the quadratic formula to solve for time yields two solutions: t = 10 s and t = −20 s. A negative value for time is unreasonable, since that would mean the event happened 20 s before the motion began, therefore we can discard that solution. Thus, the time taken by the car to travel the 200 m ramp is 10 s.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 3.4: Motion with Constant Acceleration.
Dal capitolo 3:

Now Playing
3.8 : Kinematic Equations - II
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.2K Visualizzazioni

3.1 : Posizione e spostamento
Motion Along a Straight Line
17.1K Visualizzazioni

3.2 : Velocità media
Motion Along a Straight Line
18.0K Visualizzazioni

3.3 : Velocità istantanea - I
Motion Along a Straight Line
12.2K Visualizzazioni

3.4 : Velocità istantanea - II
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.1K Visualizzazioni

3.5 : Accelerazione media
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.3K Visualizzazioni

3.6 : Accelerazione istantanea
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.5K Visualizzazioni

3.7 : Equazioni cinematiche - I
Motion Along a Straight Line
10.2K Visualizzazioni

3.9 : Equazioni cinematiche - III
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.4K Visualizzazioni

3.10 : Equazioni cinematiche: risoluzione dei problemi
Motion Along a Straight Line
11.8K Visualizzazioni

3.11 : Corpi in caduta libera: Introduzione
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.8K Visualizzazioni

3.12 : Corpi in caduta libera: esempio
Motion Along a Straight Line
15.5K Visualizzazioni

3.13 : Velocità e posizione con metodo grafico
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.2K Visualizzazioni

3.14 : Velocità e posizione con il metodo integrale
Motion Along a Straight Line
5.9K Visualizzazioni