15.6 : Strong Acid and Base Solutions
A strong acid is a compound that dissociates completely in an aqueous solution and produces a concentration of hydronium ions equal to the initial concentration of acid. For example, 0.20 M hydrobromic acid will dissociate completely in water and produces 0.20 M of hydronium ions and 0.20 M of bromide ions.

On the other hand, a strong base is a compound that dissociates completely in an aqueous solution and produces hydroxide ions. For example, 0.015 M KOH, a group 1 metal hydroxide, will dissociate completely and produce 0.015 M of OH- and 0.015 M of K+.
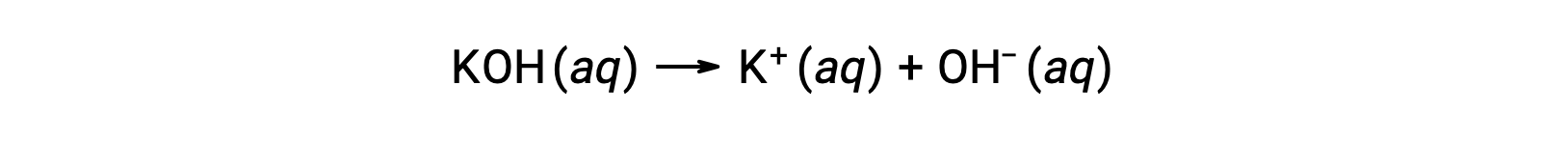
Group 2 metal hydroxides, like barium hydroxide [Ba(OH)2] and strontium hydroxide [Sr(OH)2], are also strong bases and possess two hydroxide ions. This causes them to produce a more basic solution compared to NaOH or KOH at the same concentration. For example, 0.015 M Ba(OH)2Â produces 0.015 M Ba+Â and 0.030 M hydroxide.
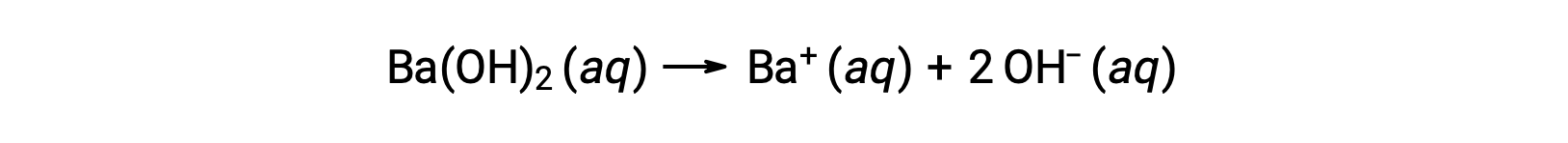
As strong acids and bases dissociate completely, molar ratios can be used to determine their hydronium and hydroxide concentrations, which in turn can be used to calculate the pH or pOH of a solution. For example, a 0.030 M HCl solution will produce 0.03 M hydronium ions. Therefore the pH of this solution will be

The pOH of the same solution can be determined using the formula

As the pH of the solution is 1.52, its pOH can be calculated as

Similarly, the concentration of hydroxide ions produced by strong bases can be used to determine the pOH of a solution using the equation

The above equation can also be used to determine the hydroxide ion concentration when pOH is known. For example, if the pOH of a solution is 3.00,
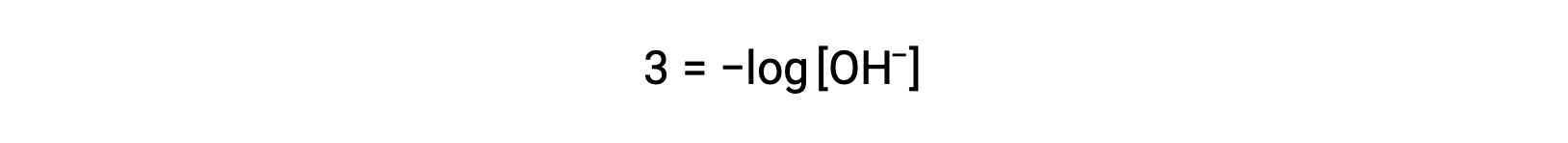
Multiplication of both sides by â1 gives

Now, take the antilog of both sides

Thus, the hydronium ion concentration of the solution with pOH 3 is 1.0 Ã 10â3 M. A similar method can be used to determine the hydronium ion concentration of a solution if its pH is known.
From Chapter 15:

Now Playing
15.6 : Strong Acid and Base Solutions
Acids and Bases
31.0K Views

15.1 : Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases
90.0K Views

15.2 : Acid/Base Strengths and Dissociation Constants
Acids and Bases
59.7K Views

15.3 : Water: A Bronsted-Lowry Acid and Base
Acids and Bases
49.4K Views

15.4 : pH Scale
Acids and Bases
67.7K Views

15.5 : Relative Strengths of Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Acids and Bases
44.9K Views

15.7 : Weak Acid Solutions
Acids and Bases
37.2K Views

15.8 : Weak Base Solutions
Acids and Bases
22.2K Views

15.9 : Mixtures of Acids
Acids and Bases
19.5K Views

15.10 : Ions as Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases
23.0K Views

15.11 : Determining the pH of Salt Solutions
Acids and Bases
43.1K Views

15.12 : Polyprotic Acids
Acids and Bases
28.6K Views

15.13 : Acid Strength and Molecular Structure
Acids and Bases
30.5K Views

15.14 : Lewis Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases
43.0K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved