A solution containing appreciable amounts of a weak conjugate acid-base pair is called a buffer solution, or a buffer. Buffer solutions resist a change in pH when small amounts of a strong acid or a strong base are added. A solution of acetic acid and sodium acetate is an example of a buffer that consists of a weak acid and its salt: CH3COOH (aq) + CH3COONa (aq). An example of a buffer that consists of a weak base and its salt is a solution of ammonia and ammonium chloride: NH3 (aq) + NH4Cl (aq).
How Buffers Work
To illustrate the function of a buffer solution, consider a mixture of roughly equal amounts of acetic acid and sodium acetate. The presence of a weak conjugate acid-base pair in the solution imparts the ability to neutralize modest amounts of added strong acid or base. For example, adding a strong base to this solution will neutralize hydronium ion and shift the acetic acid ionization equilibrium to the right, partially restoring the decreased H3O+ concentration:
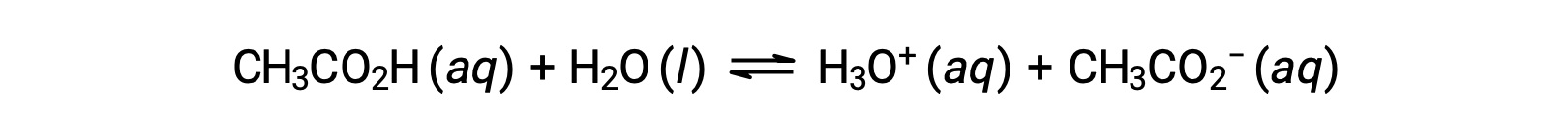
Likewise, adding a strong acid to this buffer solution will neutralize acetate ion, shifting the above ionization equilibrium right and returning [H3O+] to near its original value. Figure 1 provides a graphical illustration of the changes to the buffer solution when strong acid and base are added. The buffering action of the solution is essentially a result of the added strong acid and base being converted to the weak acid and base that make up the buffer's conjugate pair. The weaker acid and base undergo only slight ionization, as compared to the complete ionization of the strong acid and base. The solution pH, therefore, changes much less drastically than it would in an unbuffered solution.
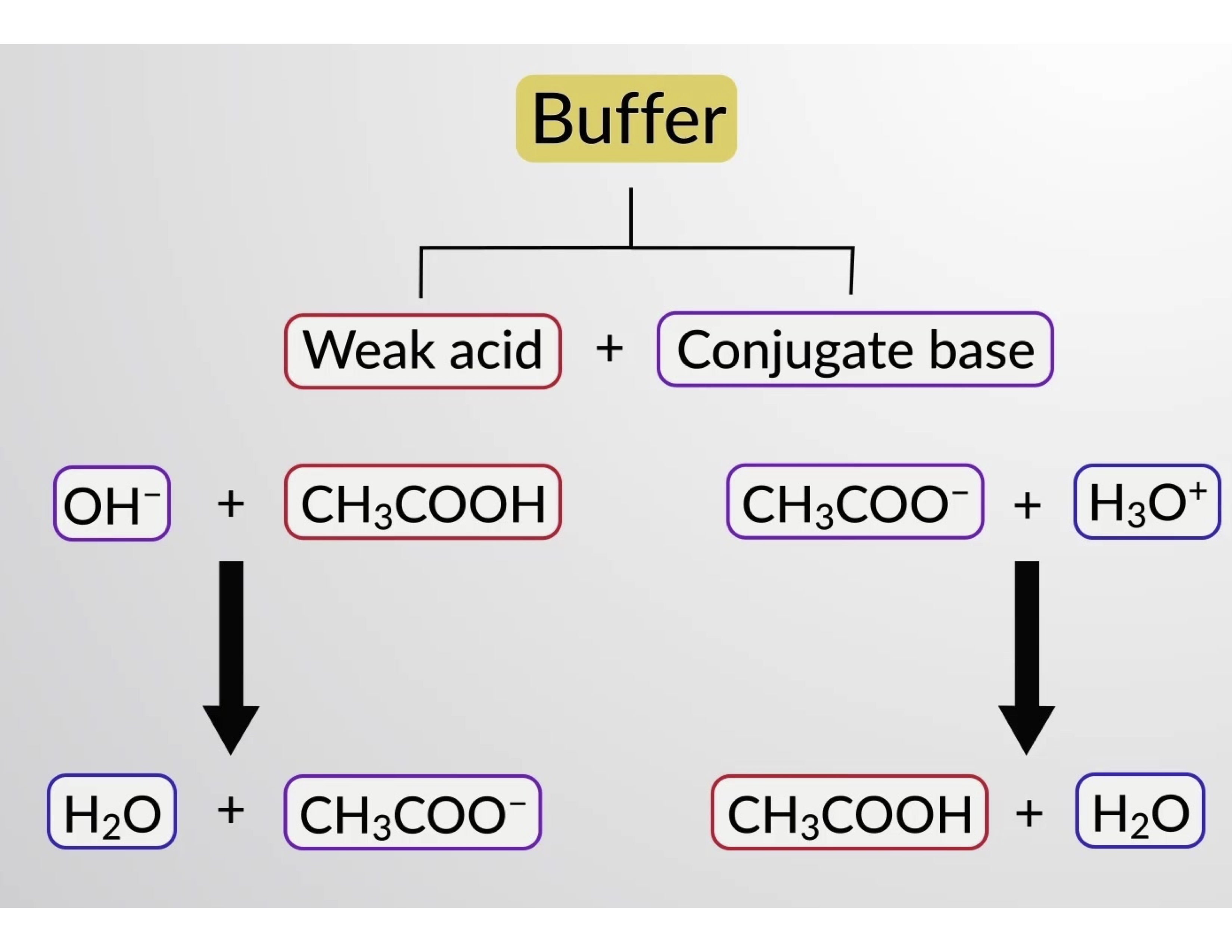
Figure 1. Buffering action in a mixture of acetic acid and acetate salt.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 14.6: Buffers.
From Chapter 16:

Now Playing
16.2 : בופרים
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
162.9K Views

16.1 : אפקט היון המשותף
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
40.6K Views

16.3 : משואת הנדרסון-האסבלך
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
67.6K Views

16.4 : חישוב שינוייpH בתמיסת בופר
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
52.2K Views

16.5 : יעילות בופר
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
48.1K Views

16.6 : חישובי טיטרציה: חומצה חזקה- בסיס חזק
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
28.7K Views

16.7 : חישובי טיטרציה: חומצה חלשה- בסיס חלש
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
43.3K Views

16.8 : אינדיקטורים
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
47.5K Views

16.9 : טירציה של חומצה רב פרוטית
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
95.4K Views

16.10 : שיווי משקל מסיסות
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
51.0K Views

16.11 : גורמים המשפיעים על מסיסות
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
32.8K Views

16.12 : יצירת יוני קומפלקס
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
22.9K Views

16.13 : שיקוע של יוני
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
27.3K Views

16.14 : אנליזה איכותית
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
19.8K Views

16.15 : עקומות טירציית חומצה-בסיס
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
125.3K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved