20.18 : Maxwell's Thermodynamic Relations
Maxwell's thermodynamic relations are very useful in solving problems in thermodynamics. Each of Maxwell's relations relates a partial differential between quantities that can be hard to measure experimentally to a partial differential between quantities that can be easily measured. These relations are a set of equations derivable from the symmetry of the second derivatives and the thermodynamic potentials.
All thermodynamic potentials are exact differentials. Therefore, their second-order derivative does not depend on the order of differentiation. In the case of Maxwell's relations, the thermodynamic potential is expressed in terms of the partial derivatives of that function. Substituting the values of the partial derivatives gives Maxwell's equations. The four Maxwell's relations are:
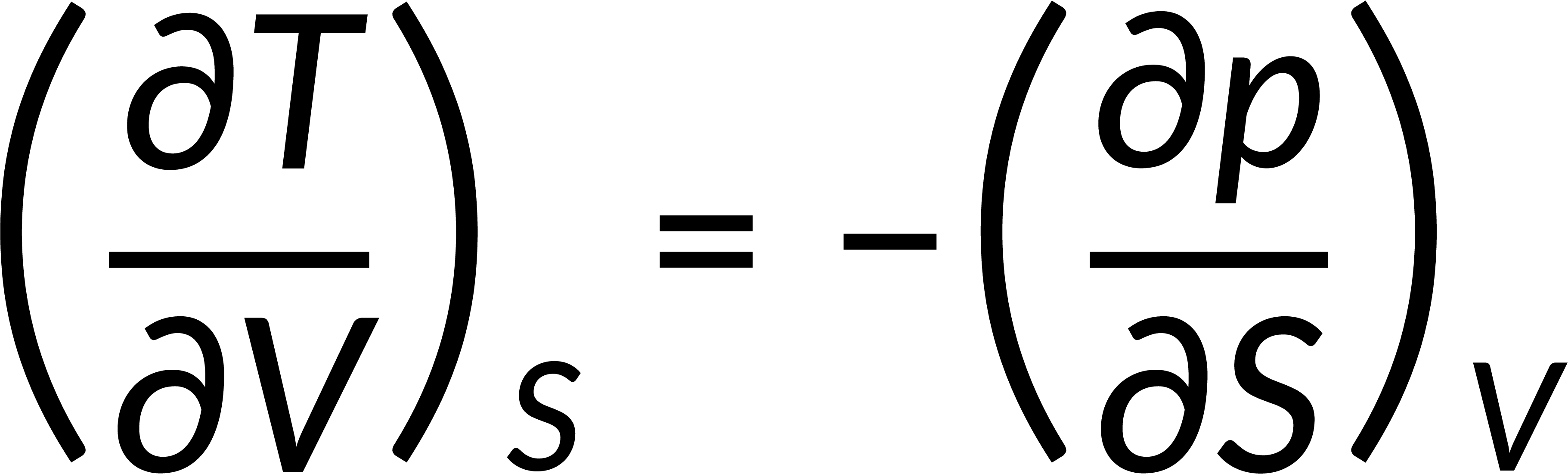
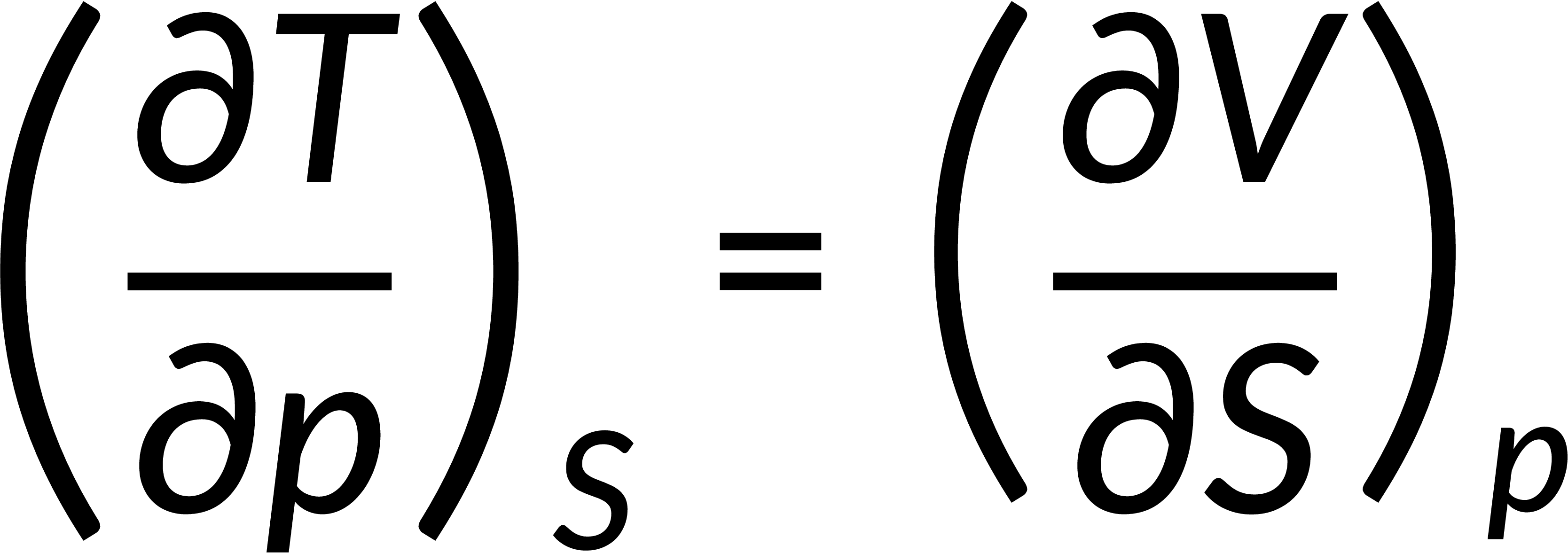
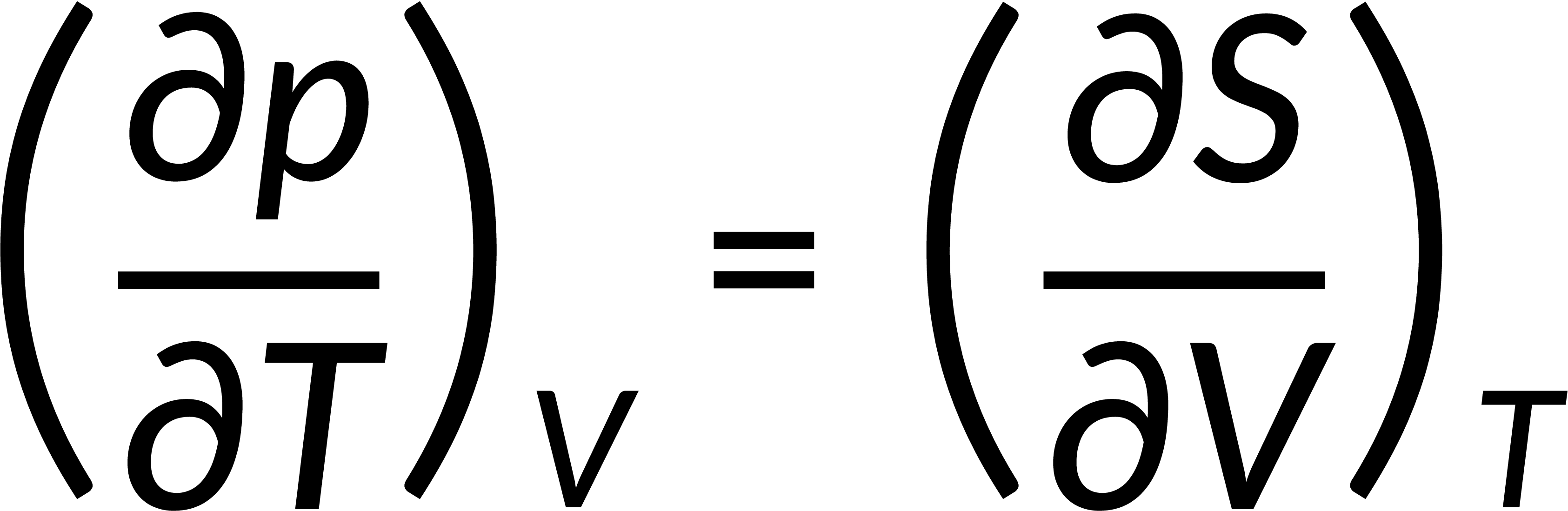
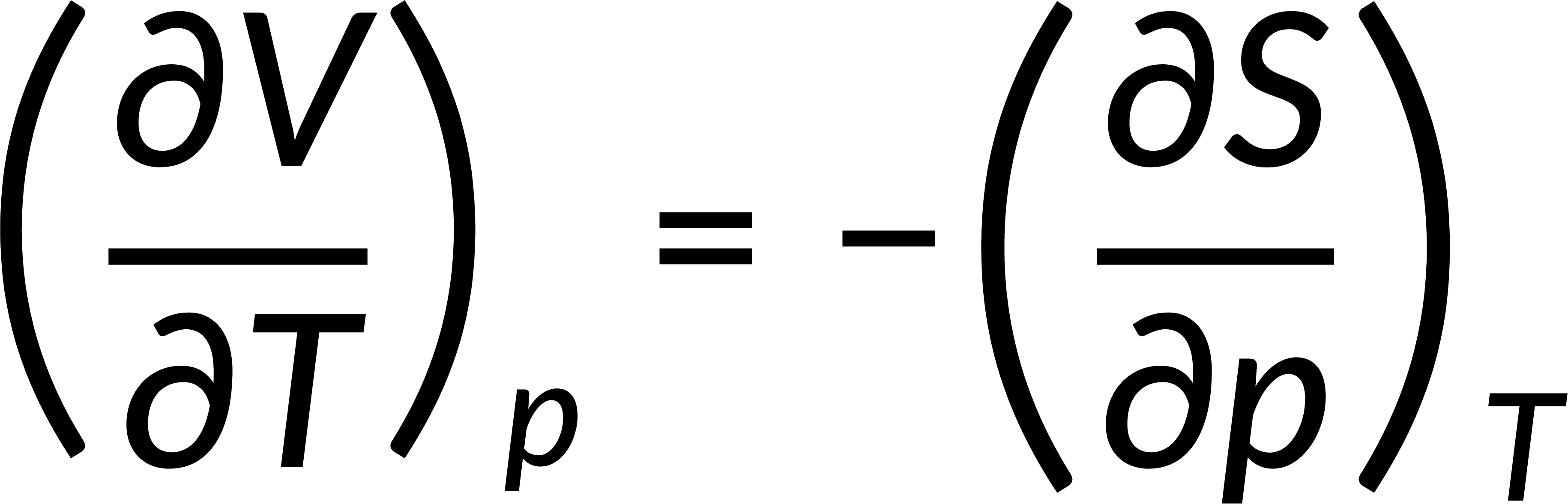
These equations relate entropy changes, which are difficult to measure, with changes in other thermodynamic variables, like temperature, volume, and pressure, that are easier to measure. For example, in the last equation, the left-hand side term gives the change in pressure with the temperature at constant volume. This quantity can be easily measured in a laboratory. However, the term on the right-hand side of the equation is more complicated, as it is hard to measure the entropy change with volume at a constant temperature.
Del capítulo 20:

Now Playing
20.18 : Maxwell's Thermodynamic Relations
The First Law of Thermodynamics
2.5K Vistas

20.1 : Sistemas Termodinámicos
The First Law of Thermodynamics
4.9K Vistas

20.2 : Trabajo realizado durante el cambio de volumen
The First Law of Thermodynamics
3.9K Vistas

20.3 : Camino entre los estados termodinámicos
The First Law of Thermodynamics
3.0K Vistas

20.4 : Calor y expansión libre
The First Law of Thermodynamics
1.7K Vistas

20.5 : Energía interna
The First Law of Thermodynamics
4.5K Vistas

20.6 : Primera Ley de la Termodinámica
The First Law of Thermodynamics
4.1K Vistas

20.7 : Primera Ley de la Termodinámica: Resolución de Problemas
The First Law of Thermodynamics
2.5K Vistas

20.8 : Procesos cíclicos y sistemas aislados
The First Law of Thermodynamics
2.7K Vistas

20.9 : Procesos Isotérmicos
The First Law of Thermodynamics
3.5K Vistas

20.10 : Procesos isocóricos e isobáricos
The First Law of Thermodynamics
3.3K Vistas

20.11 : Capacidades caloríficas de un gas ideal I
The First Law of Thermodynamics
2.6K Vistas

20.12 : Capacidades caloríficas de un Gas Ideal II
The First Law of Thermodynamics
2.4K Vistas

20.13 : Capacidades caloríficas de un gas ideal III
The First Law of Thermodynamics
2.1K Vistas

20.14 : Procesos adiabáticos para un gas ideal
The First Law of Thermodynamics
3.0K Vistas
See More
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados