14.16 : Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion
In the early 17th century, German astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler postulated three laws for the motion of planets in the solar system. His first law states that all planets orbit the Sun in an elliptical orbit, with the Sun at one of the ellipse's foci. Therefore, the distance of a planet from the Sun varies throughout its revolution around the Sun.
While in an elliptical orbit, the total energy of the planet is conserved. Therefore, the planet slows down when it is at apogee and speeds up when it is at perigee. These conclusions led Kepler to state his second law, that the radius vector of the planet sweeps out in equal areas in equal time. This means that if a planet takes the same time to travel from A to A1, and then from B to B1, then the areas AF1A1 and BF1B1 are equal, as shown in Figure 1.
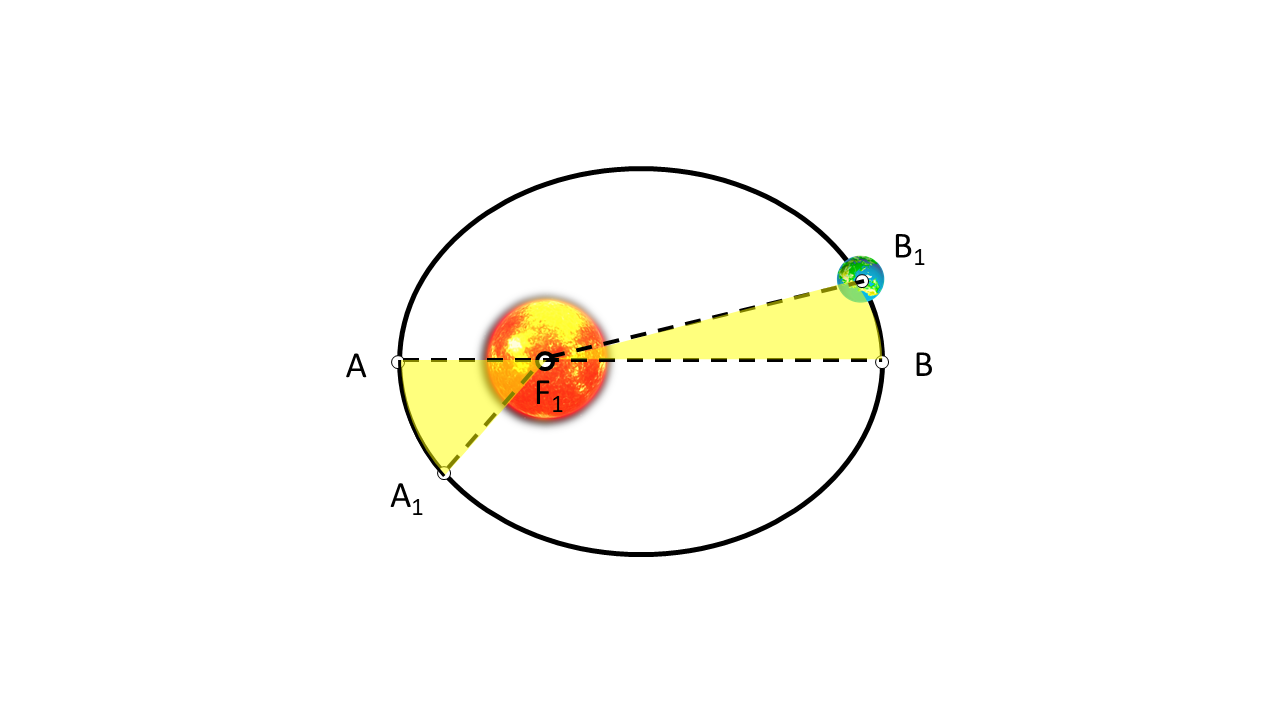
Since the area is constant in a given time interval, the planet's sector velocity remains constant. Since the sector velocity is proportional to the planet's angular momentum, Kepler’s second law implies that the angular momentum of a planet in an elliptical orbit is conserved.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 13.5 Kepler’s Laws of Motion.
Aus Kapitel 14:

Now Playing
14.16 : Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion
Gravitation
4.1K Ansichten

14.1 : Gravitation
Gravitation
6.3K Ansichten

14.2 : Newtons Gesetz der Gravitation
Gravitation
12.5K Ansichten

14.3 : Gravitation zwischen kugelsymmetrischen Massen
Gravitation
855 Ansichten

14.4 : Schwerkraft zwischen kugelförmigen Körpern
Gravitation
8.3K Ansichten

14.5 : Reduzierte Massenkoordinaten: Isoliertes Zweikörperproblem
Gravitation
1.2K Ansichten

14.6 : Beschleunigung durch Schwerkraft auf der Erde
Gravitation
10.6K Ansichten

14.7 : Beschleunigung durch Schwerkraft auf anderen Planeten
Gravitation
4.2K Ansichten

14.8 : Das scheinbare Gewicht und die Erdrotation
Gravitation
3.5K Ansichten

14.9 : Variation der Beschleunigung aufgrund der Schwerkraft in der Nähe der Erdoberfläche
Gravitation
2.4K Ansichten

14.10 : Potentielle Energie durch Gravitation
Gravitation
5.5K Ansichten

14.11 : Das Prinzip der Überlagerung und des Gravitationsfeldes
Gravitation
1.3K Ansichten

14.12 : Fluchtgeschwindigkeit
Gravitation
5.6K Ansichten

14.13 : Zirkuläre Umlaufbahnen und kritische Geschwindigkeit für Satelliten
Gravitation
2.9K Ansichten

14.14 : Energie eines Satelliten in einer kreisförmigen Umlaufbahn
Gravitation
2.2K Ansichten
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten